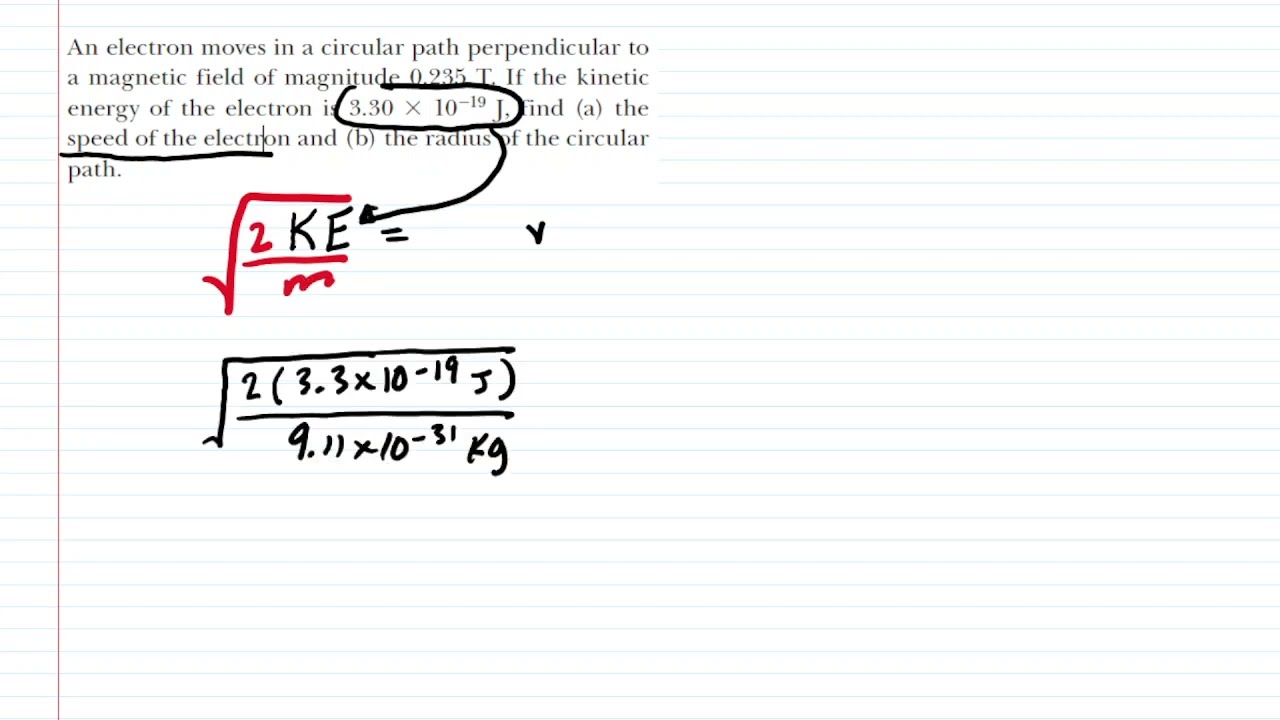
Perpendicular magnetic fields are an important concept in physics, electronics, and engineering. They are used in many applications, such as data storage, medical imaging, and electric motors. In this article, we will explore what perpendicular magnetic fields are, how they work, their pros and cons, alternatives, step by step guide to creating them, tips, and the best practices for working with them.
Table of Contents
- What is a Perpendicular Magnetic Field?
- How Does a Perpendicular Magnetic Field Work?
- When is a Perpendicular Magnetic Field Used?
- Pros and Cons of Perpendicular Magnetic Fields
- Alternatives to Perpendicular Magnetic Fields
- Step by Step Guide to Creating a Perpendicular Magnetic Field
- Comparison between Perpendicular and Parallel Magnetic Fields
- Tips for Working with Perpendicular Magnetic Fields
- Best Practices for Working with Perpendicular Magnetic Fields
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is a Perpendicular Magnetic Field?
A perpendicular magnetic field is a magnetic field that is oriented perpendicular to a surface or plane. It is represented by a vector that is perpendicular to the direction of motion of an electric charge (such as an electron). In simpler terms, it is a magnetic field that runs at a right angle to the material it is interacting with.
Key Points:
- Perpendicular magnetic field is a field that is oriented perpendicular to a surface or plane.
- It is represented by a vector that is perpendicular to the direction of motion of an electric charge.
- It is a magnetic field that runs at a right angle to the material it is interacting with.
How Does a Perpendicular Magnetic Field Work?

A perpendicular magnetic field is created when a current flows through a conductor that is perpendicular to a magnetic field. The interaction between the current and the magnetic field creates a force that causes the conductor to move or rotate. This is known as the Lorentz force.
Key Points:
- A perpendicular magnetic field is created when a current flows through a conductor that is perpendicular to a magnetic field.
- The interaction between the current and the magnetic field creates a force that causes the conductor to move or rotate.
- This force is known as the Lorentz force.
When is a Perpendicular Magnetic Field Used?

Perpendicular magnetic fields are used in many applications, including data storage, medical imaging, and electric motors. In data storage, they are used to read and write data on a hard disk drive. In medical imaging, they are used to create images of the body’s internal structures. In electric motors, they are used to generate torque and rotation.
Key Points:
- Perpendicular magnetic fields are used in many applications, including data storage, medical imaging, and electric motors.
- In data storage, they are used to read and write data on a hard disk drive.
- In medical imaging, they are used to create images of the body’s internal structures.
- In electric motors, they are used to generate torque and rotation.
Pros and Cons of Perpendicular Magnetic Fields
Like any technology, perpendicular magnetic fields have their advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a closer look:
Pros:
- High data density: Perpendicular recording technology allows for higher data densities than longitudinal recording.
- Stability: Perpendicular magnetic recording media has greater stability and lower susceptibility to temperature fluctuations.
- Durability: Perpendicular recording media has better durability, allowing it to withstand more read/write cycles.
Cons:
- Cost: Perpendicular magnetic recording technology is more expensive than other recording technologies.
- Complexity: Creating perpendicular magnetic fields requires more complex processes than other recording technologies.
- Compatibility: Perpendicular recording technology is not compatible with older devices.
Alternatives to Perpendicular Magnetic Fields
There are several alternatives to perpendicular magnetic fields, including:
1. Longitudinal Magnetic Fields:
Longitudinal magnetic fields are created when a current flows through a conductor parallel to the magnetic field. This technology is used in older hard disk drives.
2. Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording:
Heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) is a technology that uses a laser to heat up a small area of the disk surface before writing data to it. This allows for higher data densities and greater stability.
Key Points:
- Alternatives to perpendicular magnetic fields include longitudinal magnetic fields and heat-assisted magnetic recording.
- Longitudinal magnetic fields are created when a current flows through a conductor parallel to the magnetic field.
- HAMR uses a laser to heat up a small area of the disk surface before writing data to it.
Step by Step Guide to Creating a Perpendicular Magnetic Field
Creating a perpendicular magnetic field requires a specific set of tools and processes. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Choose your materials: You will need a conductor and a magnet. The conductor can be any material that conducts electricity, such as copper wire. The magnet should be strong enoughto create a magnetic field that is perpendicular to the conductor.
- Position the magnet: Place the magnet so that its magnetic field is perpendicular to the conductor.
- Connect the conductor: Connect one end of the conductor to a power source, such as a battery or power supply. The other end of the conductor should be left unconnected.
- Observe movement: When the power source is turned on, the interaction between the current and the magnetic field will cause the conductor to move or rotate.
Key Points:
- Creating a perpendicular magnetic field requires a conductor and a magnet.
- The magnet should be positioned so that its magnetic field is perpendicular to the conductor.
- Connecting one end of the conductor to a power source will create the perpendicular magnetic field.
- The interaction between the current and the magnetic field will cause the conductor to move or rotate.
Comparison between Perpendicular and Parallel Magnetic Fields
Perpendicular and parallel magnetic fields have different properties and applications. Let’s compare them:
Perpendicular Magnetic Fields:
- Used in data storage, medical imaging, and electric motors.
- Create higher data densities and greater stability than longitudinal magnetic fields.
- More complex to create than longitudinal magnetic fields.
- Not compatible with older devices.
Parallel Magnetic Fields:
- Used in older hard disk drives.
- Lower data density and stability compared to perpendicular magnetic fields.
- Easier to create than perpendicular magnetic fields.
- Compatible with older devices.
Key Points:
- Perpendicular and parallel magnetic fields have different properties and applications.
- Perpendicular magnetic fields offer higher data densities and greater stability.
- Parallel magnetic fields are used in older devices and are easier to create.
Tips for Working with Perpendicular Magnetic Fields
Working with perpendicular magnetic fields can be challenging. Here are some tips to help you get the best results:
- Use strong magnets: Perpendicular magnetic fields require strong magnets to create a strong enough magnetic field.
- Avoid interference: Perpendicular magnetic fields can be interfered with by other magnetic fields, so it’s important to keep them away from any sources of interference.
- Use shielding: Shielding can help protect perpendicular magnetic fields from interference.
Key Points:
- Working with perpendicular magnetic fields requires strong magnets and avoiding interference.
- Shielding can help protect perpendicular magnetic fields from interference.
Best Practices for Working with Perpendicular Magnetic Fields
To get the best results when working with perpendicular magnetic fields, consider these best practices:
- Keep it clean: Dust or debris can interfere with a perpendicular magnetic field, so it’s important to keep everything clean and free of debris.
- Be precise: Perpendicular magnetic fields require precision in order to work properly. Make sure all measurements are accurate and your setup is as precise as possible.
- Test your setup: Before performing any experiments or applications that use perpendicular magnetic fields, test your setup to ensure it’s working correctly.
Key Points:
- Best practices for working with perpendicular magnetic fields include keeping things clean, being precise, and testing your setup.
FAQs
- What is a perpendicular magnetic field? A perpendicular magnetic field is a magnetic field that is oriented perpendicular to a surface or plane.
- How does a perpendicular magnetic field work? A perpendicular magnetic field is created when a current flows through a conductor that is perpendicular to a magnetic field. The interaction between the current and the magnetic field creates a force that causes the conductor to move or rotate.
- What are some applications of perpendicular magnetic fields? Perpendicular magnetic fields are used in data storage, medical imaging, and electric motors.
- What are the pros and cons of perpendicular magnetic fields? The pros of perpendicular magnetic fields include high data density, stability, and durability. The cons include cost, complexity, and compatibility issues.
- What are some alternatives to perpendicular magnetic fields? Alternatives to perpendicular magnetic fields include longitudinal magnetic fields and heat-assisted magnetic recording.
Conclusion
Perpendicular magnetic fields are an important concept in physics, electronics, and engineering. They have wide-ranging applications, including data storage, medical imaging, and electric motors. Understanding how they work, their pros and cons, alternatives, and best practices for working with them can help you make the most of this powerful technology.


